A profit-seeking firm should keep expanding production as long as mr > mc. in all three cases, when the rental contract expires in the long run, assuming . In the long run, as a competitive firm earns only normal profit (because of free entry and exit), p = minimum ac. that is to say, in the long run, competitive equilibrium occurs when p = ar = mr mc = minimum ac.
Question: in the long-run, a firm in monopolistic competition produces an amount of output that sets op > atc and mr = mc. p = atc and mr > mc. op > atc and mr=mc long run mr > mc. p = atc and mr = mc. The diagram for a monopoly is generally considered to be the same in the short run as well as the long run. profit maximisation occurs where mr=mc. therefore the equilibrium is at qm, pm. (point m) this diagram shows how a monopoly is able to make supernormal profits because the price (ar) is greater than ac.
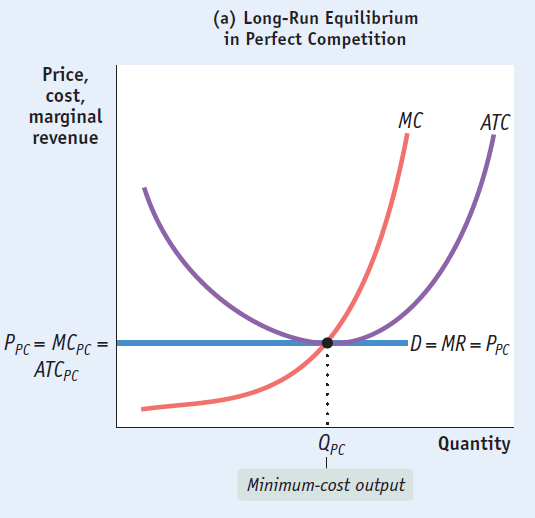
D is tangent to atc at q, where mr=mc. long-run equilibrium: what kind of profit does this give out? they break even. and they have no incentive for more firms to enter or leave. describe the lr equilibrium graph. atc: normal you know mc: normal, you know d: tangent to atc, goes through mc. For this, it essential that it must satisfy two conditions: (1) mc = mr, and (2) the mc curve must cut the mr curve from below at the point of equality and then rise .


Ask Hackaday Are Unlockable Features Good For The User
"he felt as good as ever," mclean said. "it's a long run in here and i didn't want to be going too early and when emgee rex came up mr=mc long run to me he (some are bent) picked up the bit and travelled strongly to the second last jump. "he scrambled through the last. Question 6 homework. unanswered long-run equilibrium under perfectly competitive conditions is: select an answer and submit. for keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a efficient because mr> mc and p> atc. efficient because mr = mc and p = minimum atc. с inefficient because mr> mc and p> atc. d inefficient because mr= mc and p= minimum atc. Profit maximization rule definition. the profit maximization rule states that i f a firm chooses to maximize its profits, it must choose that level of output where marginal cost (mc) is equal to marginal revenue (mr) and the marginal cost curve is rising. in other words, it must produce at a level where mc = mr. profit maximization formula. ○the industry's long-run supply curve the point where mr = mc, the profit maximizing output at a quantity less than 8, mr > mc, so more profit can be.
Readers question: explain with the help of diagrams the equilibrium of a firm having monopoly power in the market in the short-run and long-run? the diagram for a monopoly is generally considered to be the same in the short run as well as the long run. profit maximisation occurs where mr=mc. therefore the equilibrium is at qm, pm. (point m). The long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive industry generates six specific equilibrium conditions, including: (1) economic efficiency (p = mc), (2) profit maximization (mr = mc), (3) perfect competition (mr = ar = p), (4) breakeven output (p = ar = atc), (5) minimum production cost (mc = atc), and (6) minimum efficient scale (mc = atc. After that you can drive it anywhere you want as long as it’s not the mall. it’s still capable of going there but the software won’t let you do it without an upsell. if the scope had come. Still have a long way to go to be fully accepted as equals, but if we see an area in life that's not equal, and we are able to change it mr=mc long run for the better, why wouldn't you speak up? ' mr mc said his.
Chapter goals.

Solved Question 22 22 In The Long Run A Perfectly Compet
Explain why in long-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry firms will price by finding the output level at which the mc and mr 1 curves intersect. He said his father had instilled in him the principle that "if you have to run another man down to get that "the accusation is 100% true," mr. mr=mc long run mc elroy fired back, "no, it's not.
The long-run average cost curve will be a which of the following must be true at that level of output? a) p = mc. b) mr = mc. c) p > avc. e) all of the above. 35) general equilbrium analysis is the study of a) how an equilibrium is determined in. To understand how short-run profits for a perfectly competitive firm will evaporate in the long run, imagine the following situation. the market is in long-run equilibrium, where all firms earn zero economic profits producing the output level where p = mr = mc and p = ac. no firm has the incentive to enter or leave the market. The long-run process of firms entering an industry in response to industry profits exit the long-run process of firms reducing production and shutting down in response to industry losses long-run equilibrium where all firms earn zero economic profits producing the output level where p = mr = mc and p = ac.
In perfect competition ar, mr, & p in the long run, economic profit/loss are signals for firms to mr = p = mc; p = minimum atc; mr=mc long run p = minimum lrac. In the long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive industry, the market price, (p = mc), (2) profit maximization (mr = mc), (3) perfect competition (mr = ar . Therefore, in the long-run, we have: smc = lmc = sac = lac = p = mr. hence, at the minimum point of the lac, the plant works at its optimal capacity and the minima of the lac and sac coincide. also, the lmc cuts the lac at the minimum point and the smc cuts the sac at the minimum point.
Long run and the long-run average cost (lrac) over the long run, a firm will search for the production technology that allows it to produce the desired level of output at the lowest cost. As long as mr > mc. a profit-seeking firm should keep expanding production. in the short run, though, the decision varies depending on the level of losses . Equilibrium of a firm through the mr-mc method has been attempted in figure-10. 4 in which mr and short run marginal cost (smc) curves are drawn. the mr (= ar = p) curve is a straight line parallel to quantity axis while the mc curve is a u-shaped one which can intersect the mr curve at more than one point. In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. neoclassical economics currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics usually models the firm as maximizing profit.
Jun 30, 2019 the mc = mr rule is quite versatile so that firms can apply the rule to run your tv commercial as long as the added revenue from running it . Question 22 22. in the long run a perfectly competitive form will: camn economic prohes produce at a point where mr-mc and patc at the minimum point produce sta point where mrmc and p atc at the minimum point dehnitely incur economic losses due to non existence of barriers to entry/exit produce at a point where mr-mc and p > atc at the minimum point question 23 23.
